Pre-recorded Sessions: From 4 December 2020 | Live Sessions: 10 – 13 December 2020
4 – 13 December 2020
Pre-recorded Sessions: From 4 December 2020 | Live Sessions: 10 – 13 December 2020
4 – 13 December 2020
#SIGGRAPHAsia | #SIGGRAPHAsia2020
#SIGGRAPHAsia | #SIGGRAPHAsia2020










Date/Time:
04 – 13 December 2020
All presentations are available in the virtual platform on-demand.
Lecturer(s):
Adithya Pediredla, Carnegie Mellon University, United States of America
Yasin Karimi Chalmiani, Carnegie Mellon University, United States of America
Matteo Giuseppe Scopelliti, Carnegie Mellon University, United States of America
Maysamreza Chamanzar, Carnegie Mellon University, United States of America
Srinivasa Narasimhan, Carnegie Mellon University, United States of America
Ioannis Gkioulekas, Carnegie Mellon University, United States of America
Bio:
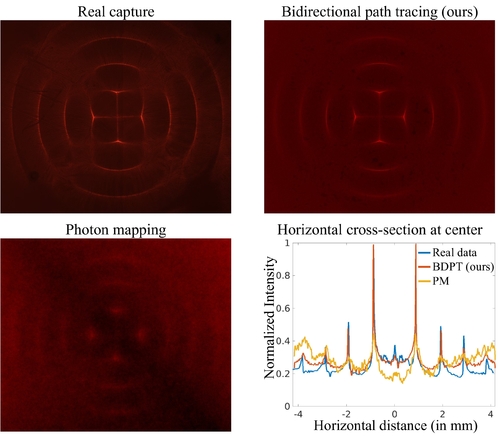
Description: Rendering radiative transfer through media with a heterogeneous refractive index is challenging because the continuous refractive index variations result in light traveling along curved paths. Existing algorithms are based on photon mapping techniques, and thus are biased and result in strong artifacts. On the other hand, existing unbiased methods such as path tracing and bidirectional path tracing cannot be used in their current form to simulate media with a heterogeneous refractive index. We change this state of affairs by deriving unbiased path tracing estimators for this problem. Starting from the refractive radiative transfer equation (RRTE), we derive a path-integral formulation, which we use to generalize path tracing with next-event estimation and bidirectional path tracing to the heterogeneous refractive index setting. We then develop an optimization approach based on fast analytic derivative computations to produce the point-to-point connections required by these path tracing algorithms. We propose several acceleration techniques to handle complex scenes (surfaces and volumes) that include participating media with heterogeneous refractive fields. We use our algorithms to simulate a variety of scenes combining heterogeneous refraction and scattering, as well as tissue imaging techniques based on ultrasonic virtual waveguides and lenses. Our algorithms and publicly-available implementation can be used to characterize imaging systems such as refractive index microscopy, schlieren imaging, and acousto-optic imaging, and can facilitate the development of inverse rendering techniques for related applications.